Sensing and VisualizingSite Hazards
Advanced Safety System for Mine Utility Vehicles
Real-time monitoring and hazard detection for maximum operational safety
Mine Safety Concerns
Understanding the critical safety challenges in mining and construction operations
Statistics
About 40% of fatalities and over 30% of injuries at mine sites involve mobile equipment (MSHA)
Fatalities
61 persons have died in accidents involving mobile equipment in the last 5 years
Unique Challenges
Equipment size and operator cab location create unique blind areas and safety risks
Blind Spots
Operators risk driving over highwalls, colliding with equipment, and striking miners
Despite industry awareness, MSHA and NIOSH statistics show a rising trend in fatalities between 2019 and 2023. Immediate action is required to reverse this concerning pattern.
Fatality Trends in Mining (2019-2023)
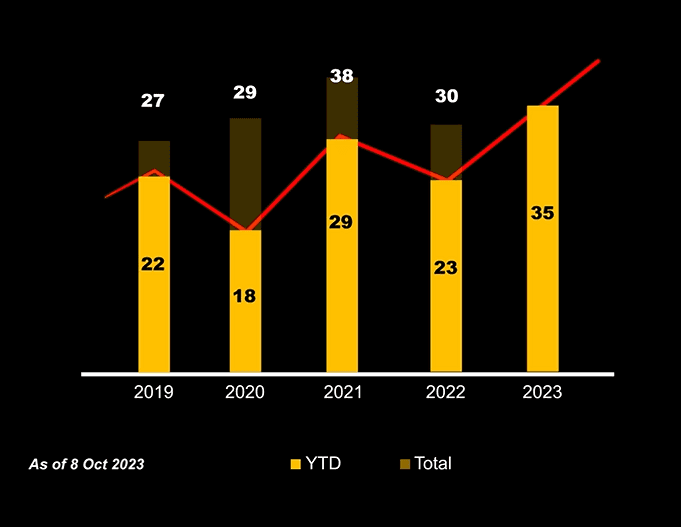
Data source: MSHA & NIOSH - Mobile Equipment Fatality Analysis
Blindspot Concerns At Mine Sites
At mine sites, the risk of accidents involving smaller vehicles is significantly high. These accidents often occur because smaller vehicles may lack adequate safety equipment and get crushed by larger vehicles with bigger blind spots.
Large mining vehicles, such as haul trucks and excavators, have extensive blind spots, making it difficult for operators to see smaller vehicles in their vicinity. This lack of visibility, combined with the absence of safety mechanisms for smaller vehicles, creates a dangerous environment for workers.
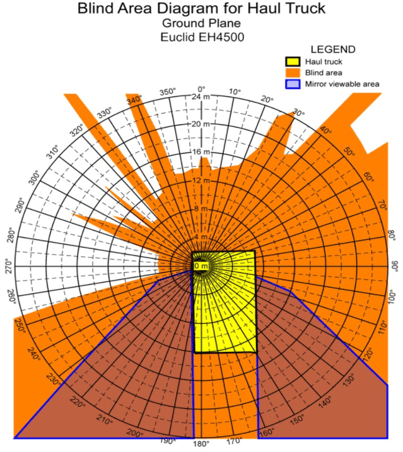
Haul Truck Blind Areas
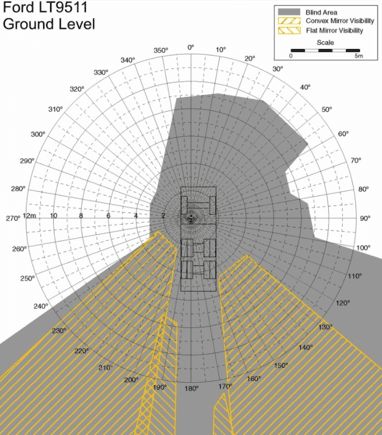
Vehicle Blind Spots
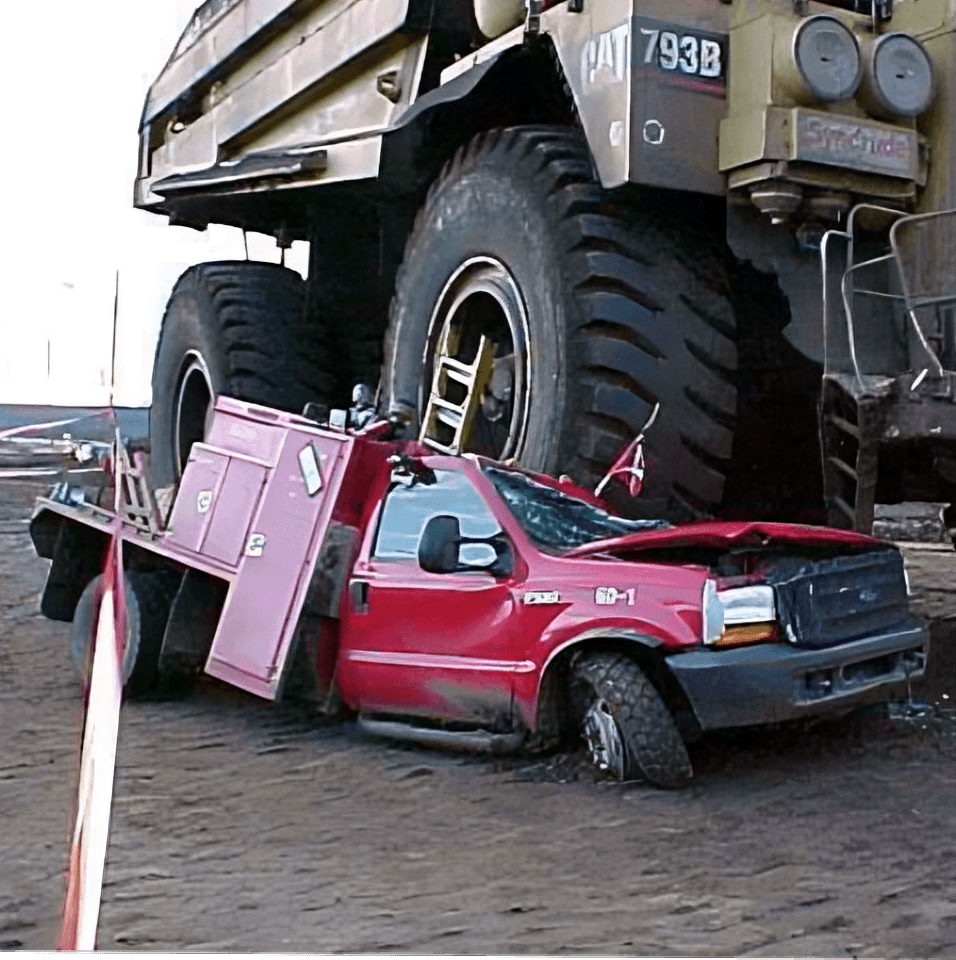

Accident Analysis 1
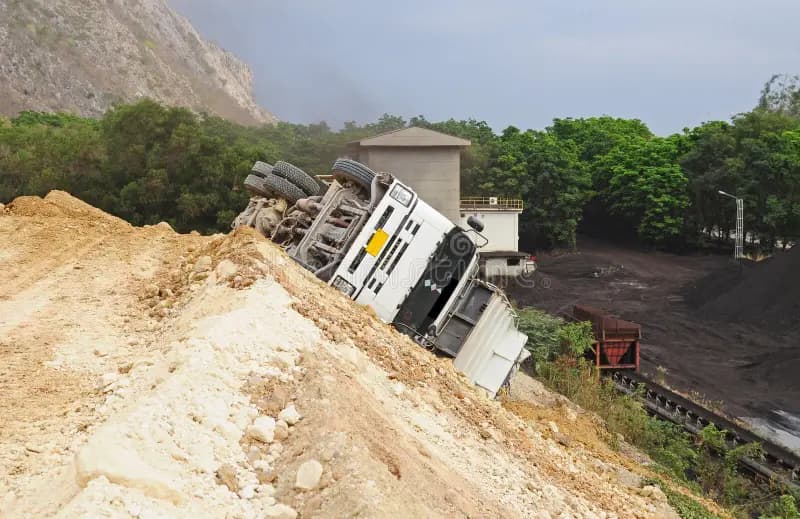

Accident Analysis 2
Key Challenges
- •Limited visibility in blind spots despite mirrors and cameras
- •High-speed equipment making emergency stops difficult
- •Inadequate communication systems between operators
- •Inconsistent safety practices across different sites
Mitigation Solutions
Enhanced Communication
Establish clear communication protocols between all equipment operators.
Comprehensive Training
Train all personnel to recognize workplace hazards and understand blind spots.
Visibility Aids
Use flags or strobe lights on smaller vehicle cabs to increase visibility.
Collision Avoidance Technology
Install and maintain collision avoidance and warning systems on mobile equipment.
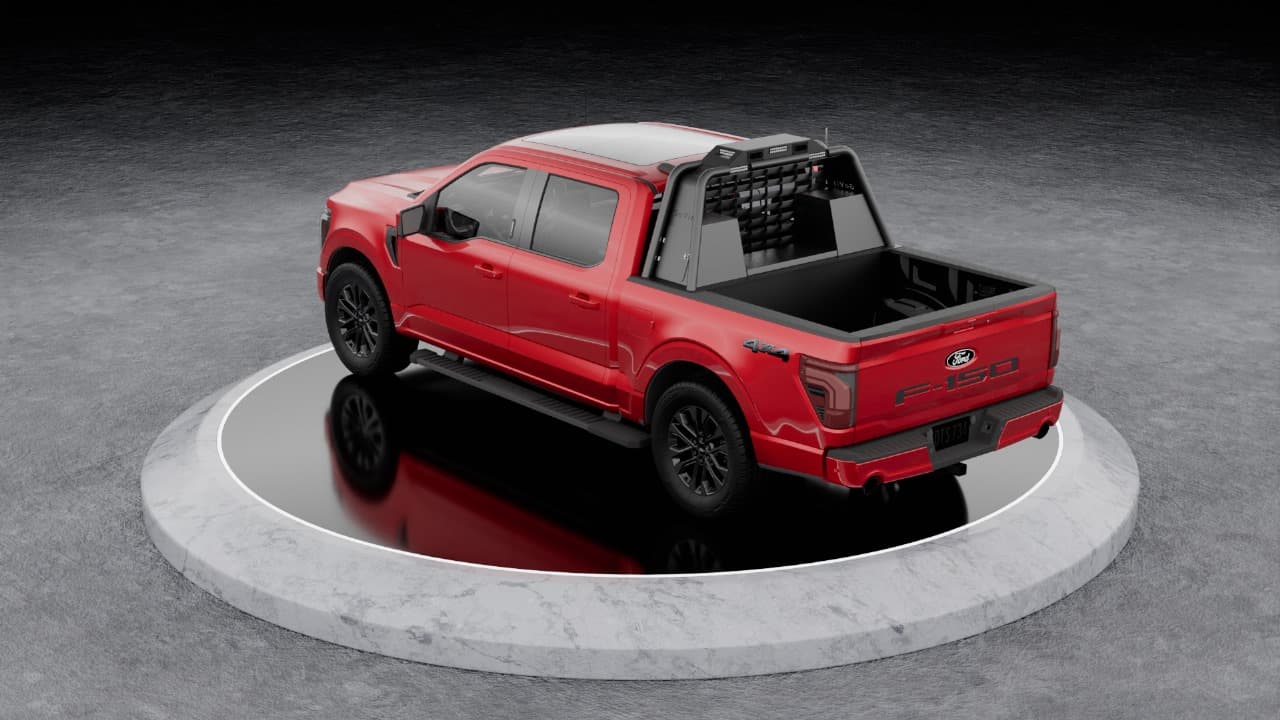

GoViz Headache Rack System
GoViz combines innovative technology in one affordable, integrated system. It's a headache rack stacked with sensors designed to help mitigate hazards in mining, construction, and outdoor recreational environments.
The device works to increase vehicle visibility, avoid collisions, and map hazardous conditions. It reduces accidents at the work site by alerting vehicle operators of impending danger and informing others of hazards encountered on the site. Many other convenient features are packed in this innovative safety solution.
MSHA Final Rule Compliance
"After reviewing comments and relevant information, MSHA believes that structuring the final rule to include a performance-based requirement to identify and analyze hazards is more appropriate than a prescriptive requirement. The performance-based approach in the final rule allows operators the flexibility to devise and tailor a safety program that is appropriate for their specific and unique mining conditions and operations."

Four Major Areas of the Final Rule
Identify and mitigate risks associated with surface mobile equipment operation.
Provide written standard operating procedures for mobile equipment operations.
Implement a hazard identification and assessment program for mobile equipment.
Ensure operators are trained and competent in mobile equipment operation safety.